- Suite 1335, 13/F.,
Central Building,
1-3 Pedder Street,
Central, Hong Kong MTR
Central Station (Exit G) - 3104 0802

-
Suite 1335, 13/F.,
Central Building,
1-3 Pedder Street,
Central, Hong Kong MTR
Central Station (Exit G) - 3104 0802
- Home
- Deep Vein Thrombosis

Deep Vein Thrombosis
深層靜脈栓塞
Deep Vein Thrombosis
There are two systems of veins: Deep veins which are embedded inside muscles and superficial veins which are just underneath our skin. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) means thrombosis (clotting) of blood in the deep veins of the legs
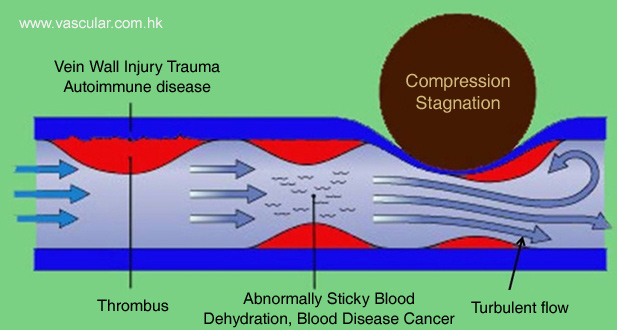
Why does deep vein thrombosis occur?
Stagnation of blood
- During walking as muscle contract blood inside the deep vein is squeezed and pushed upward. When the legs are inactive, blood stagnate in the deep veins and clotted. The longer the period of stagnation, the more likely is thrombosis. E.g. long-haul flight
Thrombophilia (Blood clots too easily), Blood becomes unusually "thick" or "sticky"
- Severe dehydration
- Congenital medical condition: such as factor V Leiden mutation, protein C deficiency, etc
- Acquired medical condition: such as cancer, after trauma, after surgery, etc
Who is at increased risk of deep vein thrombosis?
- Having had a DVT or pulmonary embolism before
- Having had a recent major operation
- After long-haul flight or prolonged bed rest
- Debilitated and immobile patient
- Pregnancy and puerperal
- Contraceptive pill or hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- Malignant disease (cancer)
- Obesity (being overweight)
- Severe heart disease
- Some blood diseases with increased tendency to clot
- Varicose veins
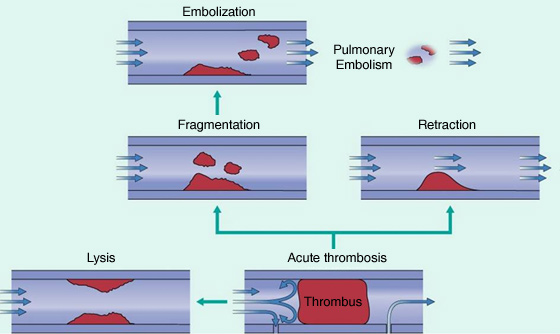
Consequences of deep vein thrombosis
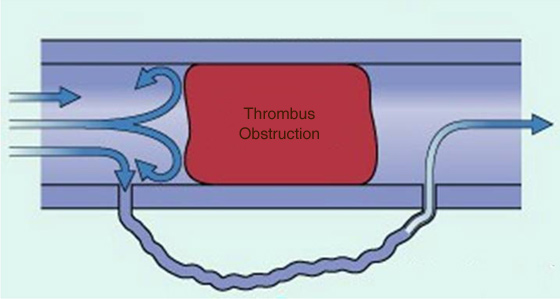
- Obstruction : Causing chronic lower limb pain, swelling, skin changes with increased pigmentation and chronic ulceration
- Blockage of the passage and pooling of blood
- Damage to the valves and allow abnormal backflow of blood
- Pulmonary embolism (PE)
- Clot (thrombus) can dislodge from the vein, and carried along the blood flow through the heart to lodge in the lungs.
- PE may cause chest pain, coughing up of blood and breathlessness.
- PE can be fatal, if a large clot lodges in the main blood vessel to the lung and blocks the return of blood to the heart
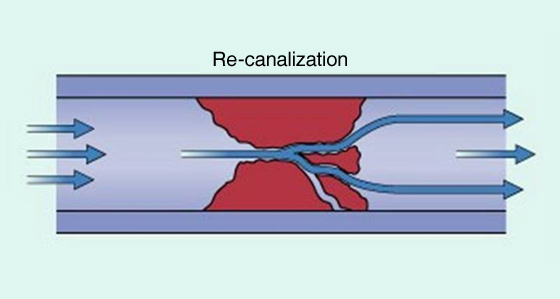
- Re-canulation of the thrombosed vein
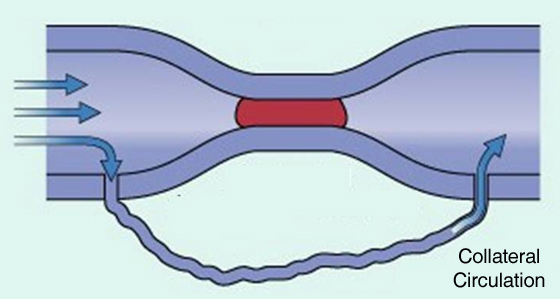
- Development of collateral circulation
What can be done to reduce the risk of DVT?
- Move your legs
Stretching and moving the legs stops blood stagnating in the deep veins of the calf Avoid prolonged standing or sitting still. Change posture, flex your feet - Don't get dehydrated.
Drink plenty of water, Avoid alcohol, which tends to cause dehydration. - Wear compression stockings
Wear compression stockings, watch out for curl up of the stocking that produce constriction - Stop smoking
Smoking increases the tendency of the blood to clot. - Anticoagulation if indicated
If you have known history of DVT or recurrent DVT, consult your doctor for possible anticoagulation therapy
Treatment for DVT
- Anti-coagulation to stop new clot from forming
- Wear compression stocking to improve circulation inside the deep vein
- Lyse or dissolve the clot for extensive thrombosis that threaten circulation